This topic covers tools and techniques for analysing data and trends in JunoViewer Web
SmartRate Deterioration Rate - Diagnostic File
|
Fritz Jooste Administrator Posts: 81
8/31/2018
|
Fritz JoosteAdministrator Posts: 81
The SmartRate Deterioration Rate calculator typically provides a more realistic/relevant deterioration rate for cases where there are anomalies in your data (e.g. un-explained improvements in data, or unexpectedly large random errors). The types of anomalies that the SmartRate calculator tries to detect and eliminate are described in this help post, which also explains how to access and use the SmartRate calculator.
When you click on the Download button next to your completed SmartRate run in the My Running Processes page, an Excel file with the following format will be generated:
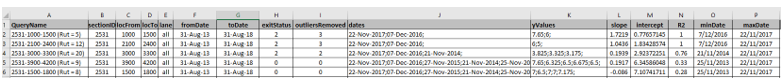
Below follows a detailed description of each column in this output file:
QueryName: contains for each row a name describing the section and location for the calculation
sectionID: contains for each row the ID of the section on which the data was calculated
locFrom: start location of the segment on which data was calculated, in metres
locTo: end location of the segment on which data was calculated, in metres
lane: lane code for the segment
fromDate and toDate: start and end dates for the range of ALL data considered in the calculation (this is determined by the "Years to go Back" specified in the input screen when you start the process)
exitStatus: a number indicating how the data was handled. The following codes apply:
-999 means there was no data, or insufficient data to get a proper trend
0 means the data was used as is, and no modification was made, in other words a regular regression gave an acceptable trend and R2 value
1 means that the R2 was at first too low, but the removal of a single outlier was sufficient to get an acceptable R2
2 means that the R2 was too low and that removal of a single outlier did not help. Some anomalies were removed but the final R2 value may or may not be OK
-888 Means that after removal or ourliers, or after checking anomalies, there was insufficient data to obtain a trend
Exit Status -888 is mostly due to the last survey point being out of line with the earlier trend. In this case, the algorithm effectively says "The data has been reset and the historical rate may no longer apply". Thus the following situation:
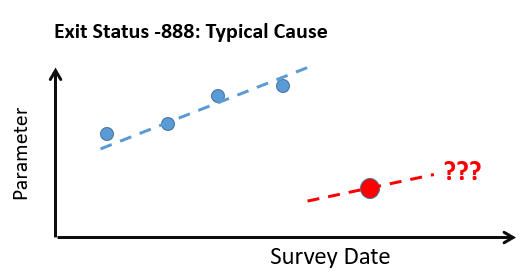
In the above an "acceptable R2" is currently set as 0.65 (meaning the fit explains 65% of the variation in the data).
outliersRemoved: indicates how many data points contained within the fromDate and toDate range were ignored in the final calculation
dates: a semi-colon delimited list of the survey dates that were used in the final calculation
yValues: a semi-colon delimited list of the parameter statistics that were used in the final calculation
slope: The final calculated deterioration rate
intercept: calculated intercept (depends on starting date used and is not really meaningful)
R2: coefficient of determination of the final regression. In our opinion, values below 0.5 indicate lots of variability and possibly these values should be overridden by a modelled estimate in the deterioration model.
minDate and maxDate: minimum and maximum dates used in the final data set after any outliers or anomalies were excluded.
edited by admin on 5/2/2019
|
|
|
0
link
|